In the digital age of healthcare, accessibility is critical. On the patient side, access to their health records, vital information, and providers drives more engagement. On the provider side, access to patient data in aggregate sets the stage for delivering a higher standard of care. These two sides of accessibility create a better patient experience — and they’re both made possible thanks to interoperability.
Interoperability is more than a buzzword in healthcare — it’s a crucial concept that needs constant attention and improvement as telehealth and digital healthcare systems evolve. Unfortunately, interoperability challenges persist in the current healthcare environment, prompting technology innovators to pursue standardizations, like DICOM.
Standardization as a means of data mobilization
Standardization levels the playing field for how healthcare data is created, formatted, stored, shared, and used. And it’s this standardization that directly enables interoperability. Interoperability, as defined by HIMSS, is the “ability of different information systems, devices and applications (systems) to access, exchange, integrate and cooperatively use data in a coordinated manner, within and across organizational, regional and national boundaries, to provide timely and seamless portability of information and optimize the health of individuals and populations globally.”
Take diagnostic imaging data, for example. A CAT scan generated on-site needs to yield the same level of insight when viewed off-site by a specialist, or even years later, when compared side by side to a current scan. That scan needs to preserve data no matter how many times it’s accessed, where it’s stored, or what applications is used to access it.
Standardizing medical data practices enables mobility and accessibility without loss of integrity. It’s why standards like DICOM exist for medical imaging data, HL7 for test results reporting, or SNOMED CT for standardizing medical terminology around the world. The goal is ubiquitous understanding, and it starts by ensuring everyone is using the same tools, following the same methods, and communicating with the same words.
Standardization is important and it has certainly helped, but it is not the sole solution needed for healthcare imagery. Interoperability is the next critical step in the process to ensure the images are safely and securely stored for easy and reliable access.

The growing importance of interoperability
Healthcare around the world is undergoing a booming technological evolution. The result is an increasing number of digital innovations, producing exponential amounts of data. Not only is this data important and insightful; it’s also deeply interconnected and critical to the delivery of patient care.
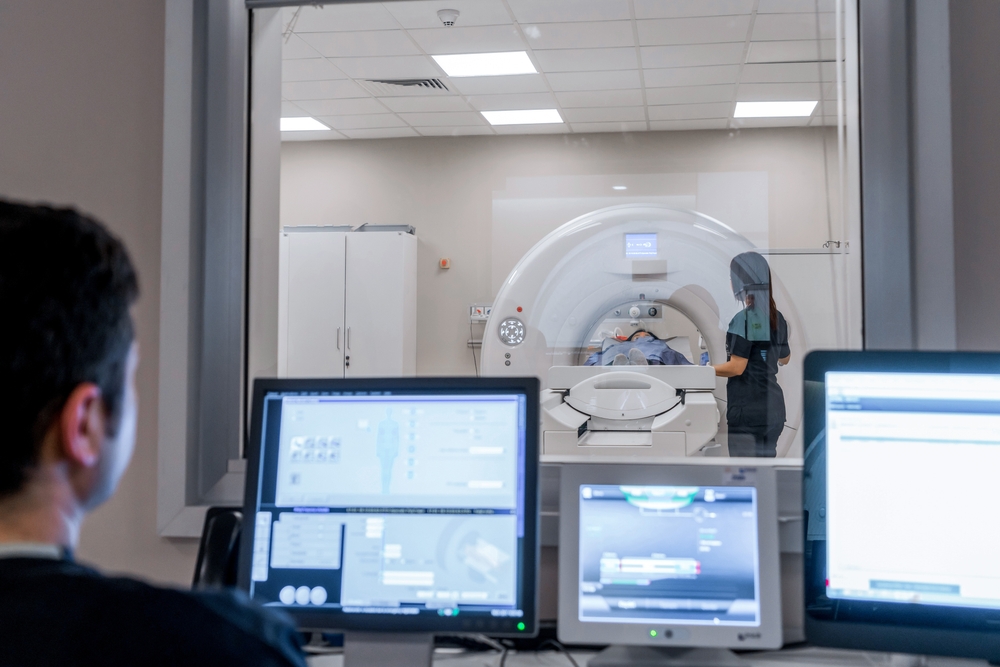
Leading the charge in generating critical data is medical imaging. As imaging technologies have evolved to include point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) and similar frontline diagnostic tools, providers have become increasingly reliant on imaging throughout the patient journey. Standardization of this data — primarily thanks to DICOM — has fueled the rise of medical imaging applications to meet demand.
But DICOM alone hasn’t necessarily created interoperability. Providers’ adherence to DICOM is what has allowed medical imaging to become more accessible across the spectrum of care. It’s one thing to move data from A to B, but if you can’t use it, you haven’t achieved anything. The cleanup of tags, file set readers, and pixel data value sets — aligned with DICOM standards — ensures images can be restored wherever they’re sent. This is critical in trauma, triage, and mission-critical situations where patients can’t afford to be rescanned.
A direct impact on the patient experience
Interoperability of healthcare data across systems has a tangible impact on patients, specifically as it pertains to outcomes and experience. For instance, interoperability of radiology — the de facto diagnostic tool — is critical, and something TeleRay provides on a daily basis. With TeleRay, healthcare teams can ensure:
- Increased speed to care
- Faster diagnosis
- Lower costs
- Less frustration
- More patient throughput
- Better outcomes
The key is ensuring radiology images are not only kept to a high standard at the point of care, but that they can be restorable to view in future healthcare events. Without this ability, patients may succumb to unnecessary rescans, slow speed to care, or, in the event of a trauma or emergency, potential fatality.
Diagnostic imaging as a frontline treatment tool, coupled with DICOM standards to ensure interoperability, marks a new paradigm for healthcare and the potential of digitized data. It allows providers to do their jobs quicker, better, and more confidently, which leads to trust, optimism, and engagement from patients. In a world of value-based care, it’s an all-important relationship — one that’s actionable at every level.
Standardization sets the standard for experience
Interoperability in healthcare is a foundational concept — one that will continue to define the patient experience as digitization becomes more prevalent across the spectrum of care. The ability to share patient data among systems, with no loss of quality or integrity, creates a level of continuity that directly benefits patients and providers alike. It’s all built atop standardizations like DICOM to create uniformity resulting in accessibility.
Learn more about the importance of interoperability at teleray.com.